Image plagiarism simply means image theft. This happens when someone copies your photos online, like copying images from your Instagram, Flickr, Facebook, your blog or any online platform and then reuse them somewhere else without properly citing those pictures. Often, they present the images as their own, completely disregarding you as the original creator and copyright holder. By failing to give due credit or citation, such individuals not only commit copyright infringement but also undermine the spirit of free sharing and responsible use on the internet. In this article, I’ll share how to track plagiarism related to images and photos using a technique called reverse image search and also a few tips to help you protect from plagiarizing your photos.
What is a Reverse Image Search? And How Does It Work?
Reverse Image Lookup is a type of Content-Based Image Retrieval (CBIR) technology that allows you to search the internet for visually similar images. Typically, when we search online, we use keywords or phrases in a search engine like Google. But with reverse image search, you upload an image instead. The search engine then scans its database, comparing the image pixel by pixel and color by color, to return a list of exact or visually similar matches found online. It’s powerful and effective method for detecting image plagiarism. I have also designed this infographic that explains how reverse image search works:
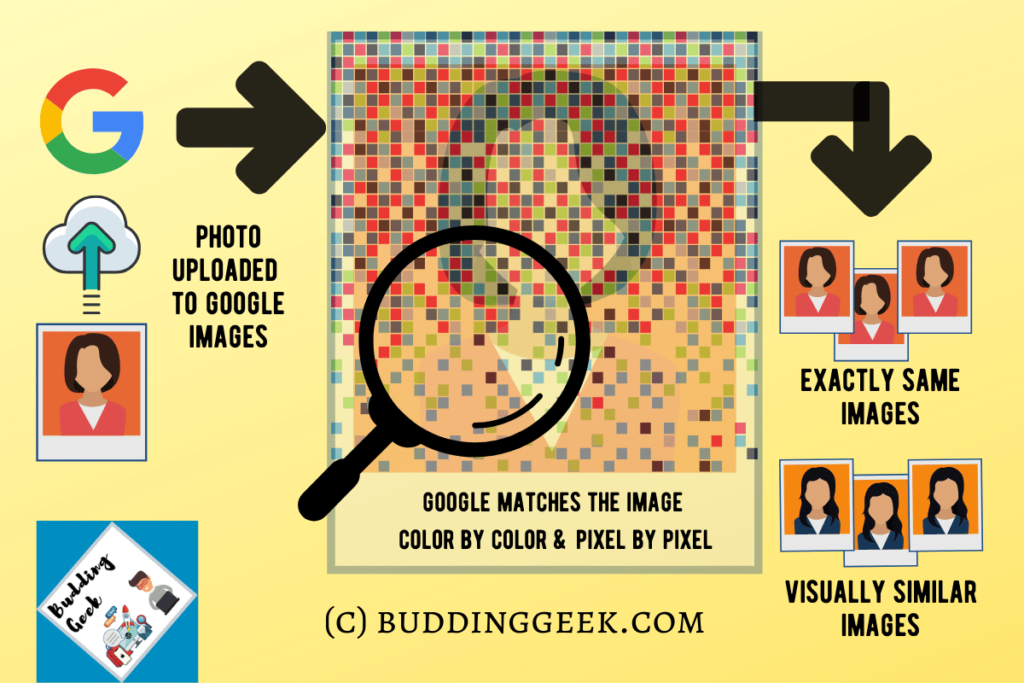
(Please cite the link of this post properly if you want to use this infographic on your website)
Important uses of Reverse Image Search:
Before we discuss the tools and techniques for performing reverse image search, let’s discuss briefly some of its important uses:
- Reverse image search helps you find out who is using your copyrighted photos across the internet without permission.
- If you come across an image and want to trace where it originally came from, this technique can point you to the source.
- If you’re working on a project and need better quality or High Definition pictures, reverse image search can help you locate high-resolution versions of the same image.
- It’s a useful tool for verifying the authenticity of profile pictures — especially helpful on social media or dating platforms where fake profiles are common.
- Want to know more about a product, location, artwork, or person in a photo? Uploading the image can give you articles, websites, or visually similar content related to it.
- Useful for journalists, researchers, or just curious readers—reverse image search can help verify whether a viral photo is real or taken out of context.
Best Image Plagiarism Checker Tools To Find Duplicate / Stolen Images Online
Now let’s review the best plagiarism checker tools on the internet that will help you find duplicate or stolen images by using Reverse Image Search:
1. Google Image Search
Google images is the first thing that comes in my mind whenever I think of reverse image search – and for a good reason! It’s credible, widely used and incredibly easy to use. Here is how it works:
Step 1: Head on to google images. There, you’ll see a small camera like icon on the right-hand side of the search bar.
Step 2: You just have to click on the camera icon and upload your desired photo that you wish to check for image plagiarism.
The search engine works on a computer technology called “query based image content” which retrieves exact/visually identical images from the basic image which was uploaded in the search query. Here is a step-by-step screenshot for your reference:


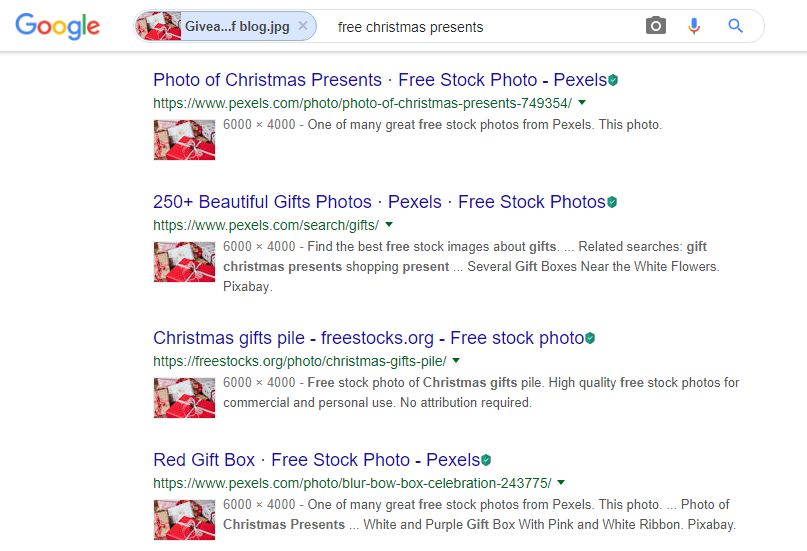
Now, a genuine question may come to mind: What if someone crops my photo or renames the file? Will Google still be able to detect that it’s my image?
The answer is yes.
Even if someone crops out a watermark from your photo or saves it with a completely different, generic filename, Google can still detect the original source. Its reverse image search algorithm focuses on the visual elements and pixel patterns of the image rather than just file names or metadata.
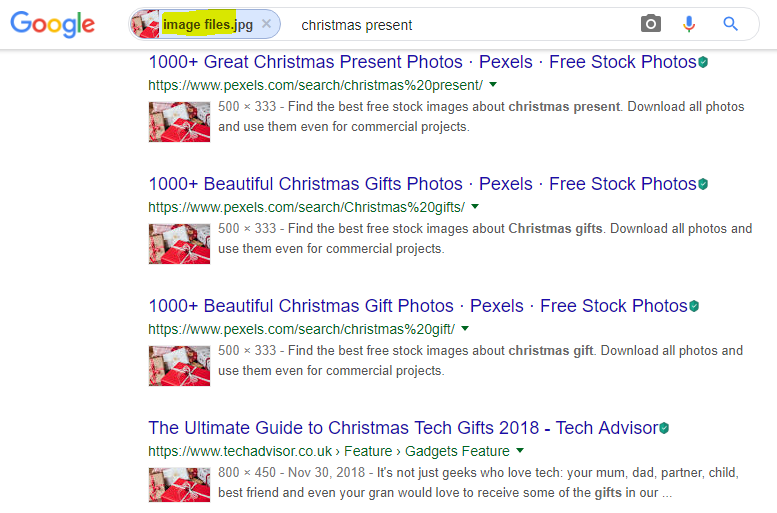
2. Yandex Image Search
When it comes to reverse image search, Yandex has an edge over Google. With a superior pixel, light, and color recognition technology, Yandex Images deliver results which are not only visually similar but also shockingly accurate. I encourage you to read and benefit from my recent post regarding how to use Yandex Images for reverse image search queries.
3. Tineye
Tineye is an exclusive reverse image search engine that claims to search images based on pattern recognition, neural networks, and machine learning technology. Like Google, Tineye crawls the web and keeps updating its data repository regularly wish fresh index of images every day. Till date, Tineye claims to have indexed over 35 billion images to its index. Tineye uses its specialized image recognition technology and compares for exact/visually similar images against its indexed database of images.
On privacy front, Tineye claims that when someone searches with Tineye, it never saves/index the images. The search is private and secure. However, as per my knowledge, Google also not saves/index the image queries.
Tineye is free to use for non-commercial purposes. However, its product lines like MatchEngine and Tineye Alerts cost as much as $200 per month, which is somewhat expensive.
4. Pixsy
Pixsy is a web service that aims at protecting the interests of photographers by regular monitoring of duplicate photos online and then keeping a provision for prosecuting the offenders if desired. It puts up a very catchy tagline – “Find and Fight Image Theft”. This is how it works:
1.) Sign up for a free account on Pixsy.
2.) Once you’ve verified your account, they will ask you to select the most appropriate representation of your business – Photographer / Graphic Designer / Online shop / Agency.
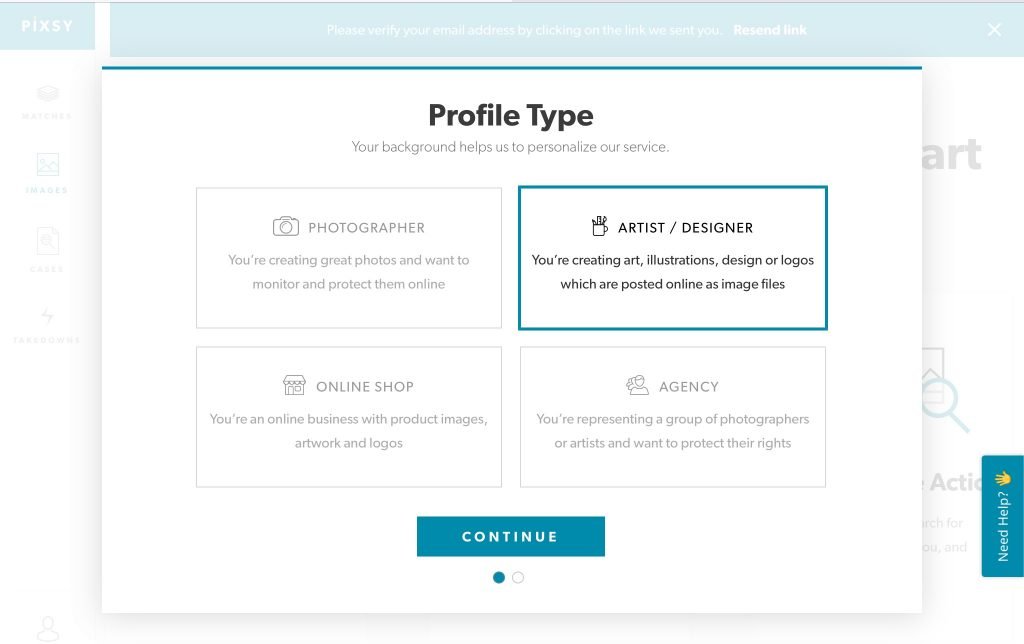
3.) You’ll get an option to either connect your photo-social networks like Instagram/Flickr/Pinterest with Pixsy or to manually upload your photos on the Pixsy server.
Once uploaded, Pixsy will start scanning the internet for exact match duplicate images. Once the scanning is complete, you’ll be shown a comprehensive report on the sources where these duplicate images have appeared.
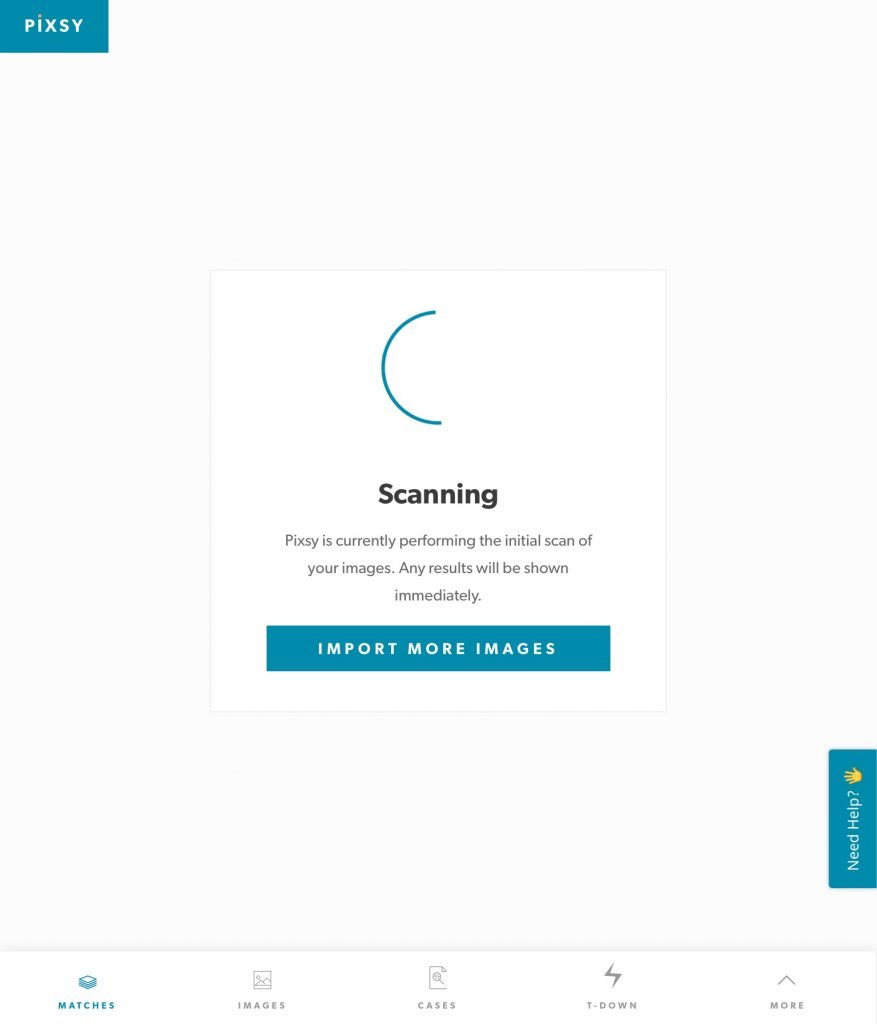
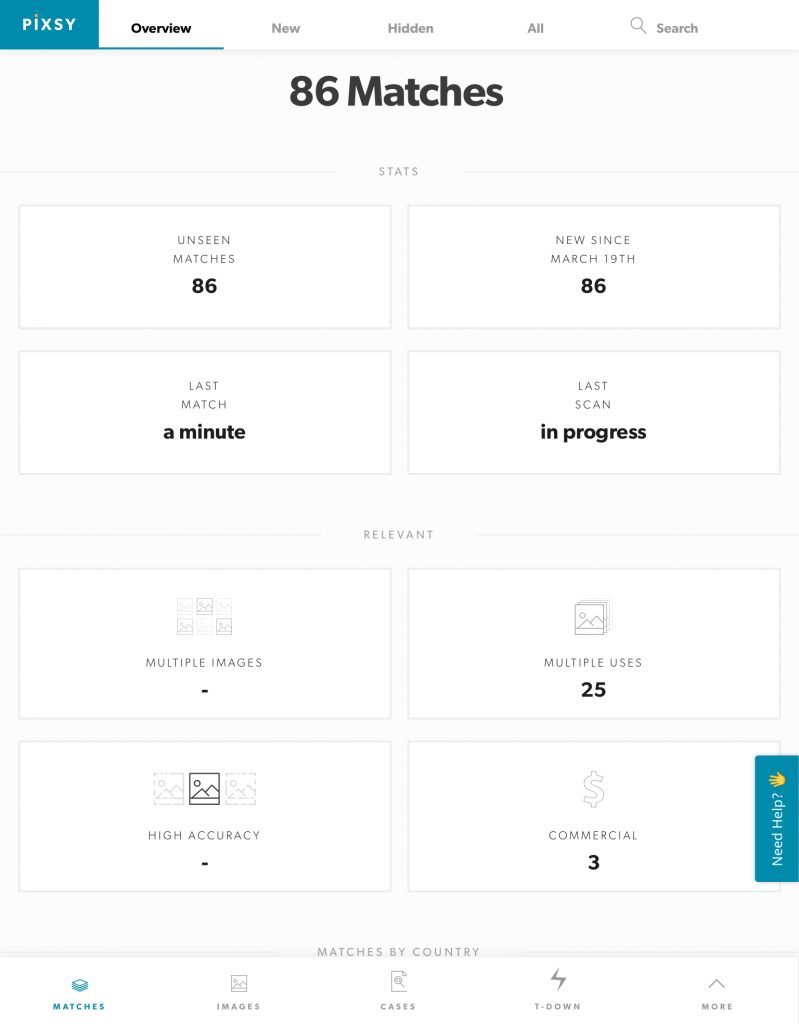
Although Pixsy offers a basic free account, but it comes with certain limitations as mentioned below:
- It monitors only 500 images
- Low priority scanning
- You can’t send takedown requests
To unlock these limitations, you must upgrade to either personal ($19/month), pro ($39/month) or advance version ($89/month) based on your individual needs.
Limitations of Reverse Image Search in Checking Image Plagiarism
While reverse image search is a powerful tool to detect image plagiarism, it does have its limitations. These tools largely depend on web crawlers being able to index image files and the web pages they appear on.
If someone uses your stolen image offline, within a private network, or on a webpage that blocks search engine crawlers, then reverse image search won’t be able to detect it. Similarly, images shared via private groups, emails, or on platforms with restricted access may also not be detectable easily.
In such cases, it becomes almost impossible to track down image plagiarism using these methods alone.
How To Prevent Image Plagiarism In The First Place?
As the old saying goes, prevention is better than cure — and this holds true for image theft as well. While we can’t control everything, there are a few simple steps we can take to reduce the chances of our images being plagiarized:
- Watermark your original photos before posting them online. It may not stop all misuse, but it adds a layer of protection and makes unauthorized use more obvious.
- Clearly mention licensing information with your images. Whether it’s Creative Commons, personal use only, or requires permission for commercial use — make sure visitors know the terms. Here is a good resource on Pixpa blog that explains it all in detail.
- Disable right-clicks on your website. While savvy users can bypass this by disabling JavaScript, it still acts as a basic deterrent, especially against casual or non-technical image thieves.
- Put a free DMCA badge on your website. It not only serves as a warning to potential content thieves but also gives you access to free watermarking and other protective services if you register.
- Use image tracking services like Pixsy, Copytrack, or TinEye Alerts to monitor where your images are appearing online.
- Upload lower resolution versions of images — If you’re sharing images just for display or preview, consider uploading slightly compressed or low-res versions. That way, they’re less useful for commercial reuse or print.
- Add copyright metadata to your image files. Before uploading photos, you can embed copyright info (like your name, website, and license details) into the image’s EXIF/IPTC metadata. Many photo editing tools can support this task.
- Finally, most important — Avoid uploading your best work publicly unless it’s absolutely necessary.
Offenders Caught? Now Issue Take-down Notices
Once you’ve identified the thieves, it’s time to contact them directly and issue legal take-down requests. Here is an ideal step-by-step process that you can follow –
- Go to their websites and find out their contact information.
- Compose a mail and politely ask them to take down the copyrighted photos. Don’t threaten them for any dire consequences. Just be polite and humble with your request.
- Wait for their responses. In case of negative responses, don’t follow up. Contact their web-hosting provider and apprise them about this issue.
- If you think the duplicate pages are hurting your reputation & SEO efforts, you can request Google to take them down from its search results.
- You may also take help from various legal take-down formats available online. Check this out on Pixsy for your reference. You can send such letters directly to the web-hosting provider/person who infringes upon your exclusive copyrights.
Recommended to read: How to do video reverse search? Step-by-step guide.
Your Thoughts?
I hope that you’ll find this article really helpful in protecting your digital assets. I look forward to engaging with you in the comments below.

very nice and knowledge able
Hi Abishek,
Great to see your post and got enlightened.
I am a Biology Researcher.
I have a query to address.
There have been occasions, wherein people copy a content from some other source and paste it as a image and merge it in a PDF file for publications.
Usually the plaigarsim count varies between softwares and servers.
If I wish to check plaigarism for an image file containing words, How can go about with it?
Thanks for your patience…
Hi MANIVANNAN,
I am sorry that I missed your comment.
With regard to your query, I believe it will be very hard for the search engines to correctly identify text between two visually similar images. They all work on OCR technology and search for plagiarism in photos going by pixel-to-pixel and color-to-color details. Distinguishing text from the images will be hard in my opinion.
it’s really good.
Hi Abhishek. Thanks for this awesome post.
Great post and very helpful for photographers. I created a site that automatically searches for your images at set intervals. No more manual uploading one-by-one. Check it out at http://www.SecureMyPics.com. Thanks.
As an avid user of google chrome for many years,i have been using the “search google for this image” and “search by image”.Google can be pretty stupid when it comes to searching images.I have came across many images that i have taken directly from the internet and searched for it looking for a larger image only for google to not recognize the image at all and name it as something else.
I will be up front with you all.I am literally a photo thief.No,i do not re-upload them to the internet or claim them as mine or sell them for profit.I just keep them for my personal use.I have years of experience in photo manipulation and hacking.I can take almost any picture and remove it’s watermark.I track every photo right down to the author’s website and every site he/she has ever uploaded it to.This includes your facebook page,flikr,500px,even smugmug.(yes,you can take any photo from smugmug also)
So here is my advice to all you photographers.please take heed to it.
1. Never upload/post anything larger then half of it’s original dimensions.You should make it as small,but as visible as possible.Anywhere from 400 to 600px should do.
2. Watermark it using different semi transparent colors.Not just one.Your watermark should cover a majority of your image.Dont put your watermark at the very bottom/top.It is too easy to crop or remove it that way.
3. Upload to one site and one site only.Do not give permission for any other vendor to sell your images.I will tell you why,and this is something most photographer’s never think about.
If your image is uploaded to sites like shutterstock,depositfiles,123rf,bigstock..etc,they all have their own watermarks and their images are different sizes.you can get most of the images at the size of a computer generated desktop wallpaper.If you take the same image from each site,resize and crop them so they are the exact same size,overlay them in photoshop,one by one,then you can remove the watermarks as they are in different areas of each photo.Eventually you will come out with a clean photo.I know as i have done this many times.
4. If you are using your own website,disable “right clicking” on every page.right clicking in chrome and using the inspect/application/top/images will get your images stolen.However,this can not be completely avoided as there is a shortcut key which also brings up the same window.That being ctrl/shift/c.
This is also a way of getting the largest image you have uploaded even though you may have hidden it.This is also why you should only upload small images.
5. Never sell your pictures directly from your website.Another words,in order for them to buy a photo,they must email you and you can send them the image through email after you have received payment.
6.If you want to post your photo’s in facebook,flikr,smugmug..etc..make sure they are the EXACT same size,with the watermark that you have uploaded to your own website.NEVER upload a larger image ANYWHERE.
It is easy for a hacker to shrink an image but not enlarge it as it will become pixellated.That is another reason for the small watermarked size.
THERE IS NO SITE SAFE FROM THEFT! as long as you take the precautions and advice i have given you,you will be more secure and photo theft free.
I welcome your responses and would be more then happy to answer any questions if i can.
Hi Damienne,
Thanks for giving such a detailed description of precautions to be taken to avoid image plagiarism. This can be truly useful and valuable for everyone 🙂
You are welcome.I am more then happy to help.And thankyou 🙂
On a side note,the site below will give you many options on how to protect your copy wright material.There ia alot of great material to read through.
http://www.naturefocused.com/articles/image-protection.html
is very good “Track Duplicate Images Using Google”
Thank you so much for sharing the list of Plagarism checker tools. Recently I faced a bitter experience when someone copied my posts. I am thankful to my friends like you who have taken initiative to come up with these kinds of posts in order to detect and stop plagiarism.
I knew this thing before lol but i want to know how you will check the originality of a picture specially in the case of thesis and research. Like one doesnt get some results and so takes a picture of some plants or bacteria from the net and set it in his own thesis or paper by editing it (croping, zooming or berightening) ?? How you will catch that plagiarism??
Hi Asif. Thanks for dropping your comment. If that research work has been published on the internet or indexed by Google, then you can easily catch that plagiarism using this tip. Otherwise, it may go undetected. Who will probably never know who is using the copyrighted photos (unless that work is published on the internet). I hope I answered your question 🙂
There are so many website on the net based on similar category, so it is obvious that a common image can be found in many sites…
what is the best way of using photos from another website? Can i use photos from the official site? As you can see my site is a site based on mobile information. So how i can i collect photos that need to put into my site?
Hi Shahadat, you can use photos from the official sources as long as you agree to their copyright conditions (if any), like linking back to the original source, attribution, etc. If there’s nothing mentioned regarding the copyrights, then you are free to use those images. However, linking back or mentioning the original source of the image is always ethical and it doesn’t hurt at all. But make sure that you’re linking/mentioning the “original source” only.
That’s one way to do this, but there are also tools for searching duplicates of pictures online, for example this one and I don’t know which method is better, because I guess that in either case there is a way of beating the system… Just like someone mentioned above, by cropping the picture or something like that.
what about the images cropped and than merged with other pics?
then*
Hi Nazneen, very good question. Do you mean creating a collage from various cropped images? I think then google search might not give the desired results. I need to look into this situation! Thanks for your thoughtful comment! 🙂
It’s Really useful for me
Thank you Great Post
I’m glad that it helped you 🙂
Great post – it’s always nice to see an informative article with a good set of images. I’ve included your post in my website “How to do a reverse image search” – see http://www.squidoo.com/reverse-search-image (Articles about Reverse Image Search) – I hope you get some visitors!
That’s appreciated! Thanks 🙂
Awesome! I really didn’t know that image plagiarism could be so easily detected with Google. But there is one question though – will it also work for re-sized images that well?
Daniel – Yes, it does works very well for re-sized images too 😉
Thank you so much for this post Abhishek! I’m a photographer based in London and this is really gonna help me a lot in finding out those who are using my work without any permission 😉
Good luck chasing the offenders 😉